Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Forearm
 Symptoms
Symptoms- Pain usually occurs in bilateral forearms
- Swelling usually occurs in bilateral forearms
- Stiffness usually occurs in bilateral forearms
 Causes
Causes- Unknown
- Autoimmune disease
- Possible family heredity
- Usually it takes a chemical or environmental "trigger" to activate the disease in people who genetically inherit RA
 Treatment
Treatment- ROM and stretching to forearm
- Upper extremity strengthening
- Hand intrinsic muscle strengthening
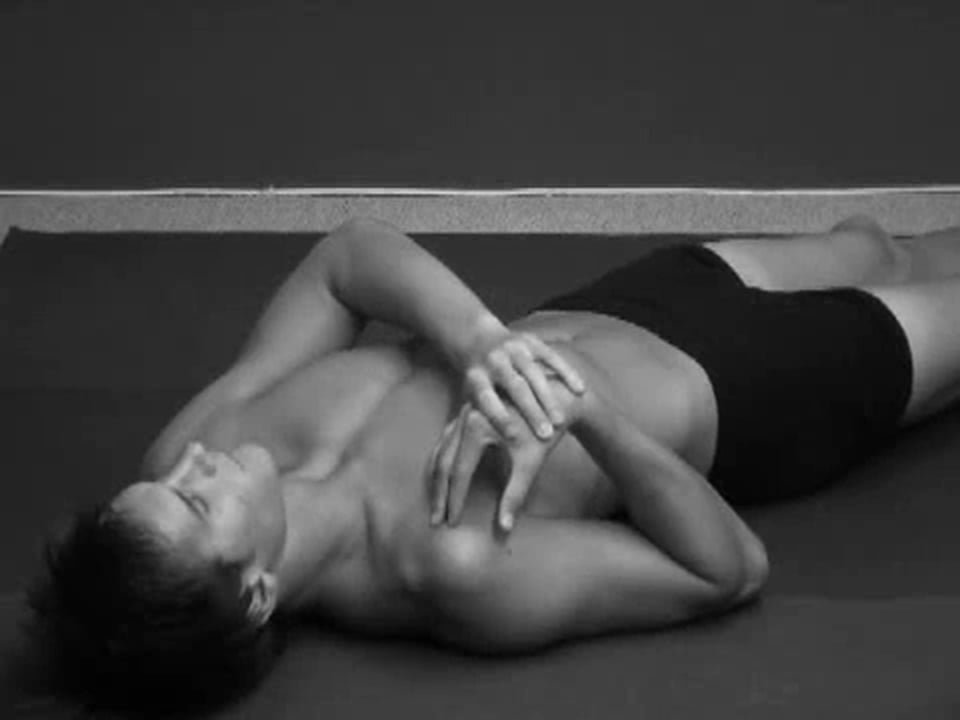

- Elbow Flexion Stretch
- Passive Elbow Extension
- Elbow Pronation Stretch
- Elbow Supination Stretch
- Full Anterior Stretch
- Wall Clocks
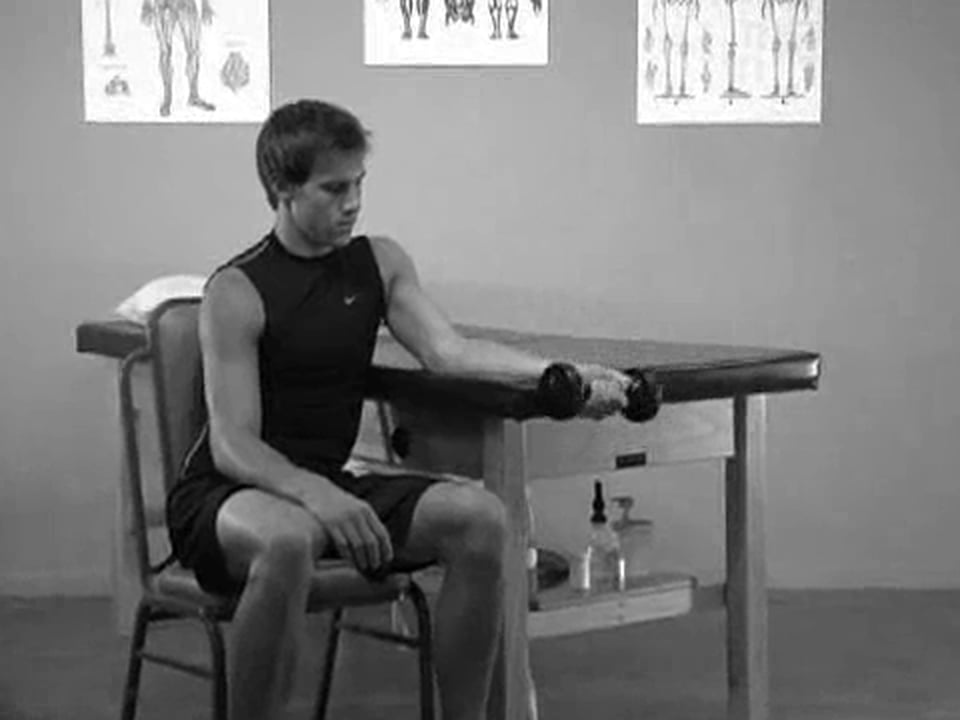

- Wrist Curls
- Wrist Pronation Supination
- Ulnar Radial Deviation
- Rice Wrist Flexion And Extension
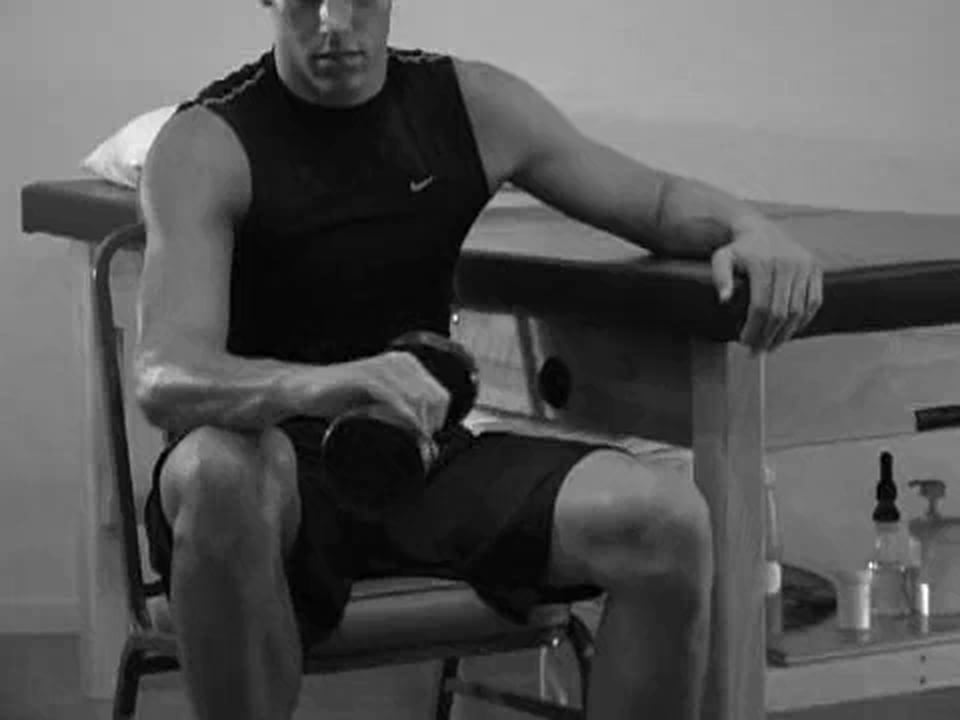

- Ulnar Radial Deviation
- Rice Wrist Flexion And Extension
- Wrist Curls
- Rice Wrist Pronation Supination
- Rice Hand Opening Closing
- Eccentric Wrist Flexion
- Eccentric Wrist Extension